1999 Key Findings
National Findings
In this year's report the United States received:
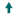 |
12 arrows pointing upward for significant improvement; |
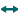 |
11 horizontal arrows indicating where there has been no significant change in performance; and |
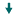 |
5 arrows pointing downward for significant declines in performance. |
Areas of improvement
The 12 arrows that were awarded for significant improvement are associated with Goals 1, 3, 5, and 7:
Goal 1: Ready to Learn
 |
The proportion of infants
born with one or more of four health risks has decreased. |
 |
The percentage of 2-year-olds
who have been fully immunized against preventable childhood diseases has
increased. |
 |
The percentage of families who are reading and telling stories to their
children on a regular basis has increased. |
 |
The gap in preschool participation between 3- to 5-year-olds from high- and low-income families has decreased.
|
Goal 3: Student Achievement and Citizenship
The percentages of students who are proficient in reading has risen in:
 |
Grade 8. |
 The percentages of students who are proficient in mathematics have risen in:
The percentages of students who are proficient in mathematics have risen in:
 |
Grade 4; |
 |
Grade 8; and |
 |
Grade 12. |
Goal 5: Mathematics and Science
The proportion of college degrees awarded in mathematics and science has increased. This is true for:
 |
all students; |
 |
minority students; and |
 |
female students. |
Goal 7: Safe, Disciplined, and Alcohol- and Drug-free Schools
 |
The percentage of students
who report that they have been threatened or injured at school has decreased. |
Areas of decline
The 5 arrows that were awarded for significant declines in national performance are associated with Goals 4 and 7:
Goal 4: Teacher Education and Professional Development
 |
The percentage of secondary
school teachers who hold a degree in their main teaching assignment has
decreased. |
Goal 7: Safe, Disciplined, and Alcohol- and Drug-free Schools
 |
The percentage of students reporting that they used an illicit drug has increased.
|
 |
The percentage of students
reporting that someone offered to sell or give them drugs at school has
increased. |
 |
The percentage of public school
teachers reporting that they were threatened or injured at school has increased. |
 |
A higher percentage of secondary
school teachers report that student disruptions in their classrooms interfere
with their teaching. |
State Findings
Areas of improvement
In this year's report 23 states received 10 or more arrows pointing upward for significant improvement during the 1990s. Colorado, Connecticut, Kentucky, and North Carolina led the states, with significant improvement on 13 measures, followed by California, New York, South Carolina, and Texas, with significant improvement on 12.
Key improvements made by states during the 1990s are as follows:
Goal 1: Ready to Learn
|
|
37 states reduced the percentage
of infants born with one or more of four health risks. |
|
|
50 states increased the percentage
of mothers receiving early prenatal care. |
|
|
49 states increased the proportion
of children with disabilities participating in preschool. |
Goal 2: School Completion
|
|
13 states have reduced their high school dropout rates. |
Goal 3: Student Achievement and Citizenship
|
|
27 states increased the percentage
of 8th graders who are proficient in mathematics. |
|
|
50 states increased the proportion
of scores on Advanced Placement examinations that were high enough to qualify
for college credit. |
Goal 4: Teacher Education and Professional Development
|
|
17 states increased the percentage
of public school teachers who received support from a master or mentor teacher
during their first year of teaching. |
Goal 5: Mathematics and Science
|
|
51 states increased the percentage
of degrees earned by all students that were awarded in mathematics or science.
|
|
|
38 states increased the percentage
of degrees earned by minority students that were awarded in mathematics
or science. |
|
|
51 states increased the percentage
of degrees earned by female students that were awarded in mathematics or
science. |
Goal
6: Adult Literacy and Lifelong Learning
|
|
10 states increased voter registration.
|
|
|
39 states increased the percentage
of high school graduates who immediately enrolled in college. |
Goal 8: Parental Participation
|
|
17 states increased the influence
of parent associations on public school policies. |
Areas of decline
Areas in which large numbers of states showed significant declines in performance during the 1990s are as follows:
Goal 1: Ready to Learn
|
|
In 36 states, the percentage
of infants born at low birthweight has increased. |
Goal 2: School Completion
|
|
In 10 states, the high school
dropout rate has increased. |
Goal
6: Adult Literacy and Lifelong Learning
|
|
In 11 states, lower percentages
of students are enrolling in college immediately after high school.
|
Goal
7: Safe, Disciplined, and Alcohol- and Drug-free Schools
|
|
In 16 states, higher percentages of students report using marijuana. |
|
|
In 15 states, higher percentages
of students report that drugs are available on school property. |
|
|
In 37 states, higher percentages
of public school teachers report that student disruptions in class interfere
with their teaching. |
Highest-performing states
The states that were most frequently among the top performers on measures of progress toward the National Education Goals were Maine (21 times), Connecticut (20 times), and North Dakota (17 times).
Most-improved states
The states that ranked among the most-improved states the greatest number of times were Connecticut and the District of Columbia (8 times each), and North Carolina (6 times).
|